Driving efficient product development that meets regulatory standards.
Formulation strategy involves designing and developing a biopharmaceutical to ensure its safety, efficacy, and stability. Quality by Design (QbD) and Design of Experiment approaches for Formulation strategy can be applied. As with our other services, it’s important to factor that all data can feed into machine learning models for Quality by Digital Design and Quality by Prediction purposes.
Take away a copy of our guide here.
Formulations Meet Pharmaceutical & Administration Requirements
Biopharmaceutical formulation development begins by aligning the drug product with intended administration routes - oral, injectable, topical, IV, etc. Requirements include viscosity, pH and osmolality. Ideally simple formulations must support safe, efficient delivery while meeting regulatory expectation.
Safe & Painless
Patient comfort and safety are core design goals. This includes minimising site pain during dosing, optimising pH and osmolality, and using accepted excipients. If well-formulated, a product should enable painless administration, especially for injectable or sensitive applications, as well as keeping the product stable and efficacious.

Compounding
Compounding involves combining multiple components to create a final, usable dosage form. This process must be traceable, robust and performed under defined conditions. Each excipient used must be compatible and stable to ensure it contributes to a consistent and safe final drug product.
Drug Substance and Drug Product Shelf Life
Shelf life is established through testing that defines how long a substance remains safe and effective. This is important for both the drug substance and final product. Expiry or re-test dates are based on analysis of multiple stability studies performed under different storage conditions that reflect future use.
Stability Assessment's
Stability studies use real-time and accelerated conditions to evaluate how a formulation performs over time. Forced degradation and stability-indicating methods should identify breakdown products as well as define limits. These assessments support labelling, shelf-life and storage recommendations based on robust data sets that have been statistically analysed.
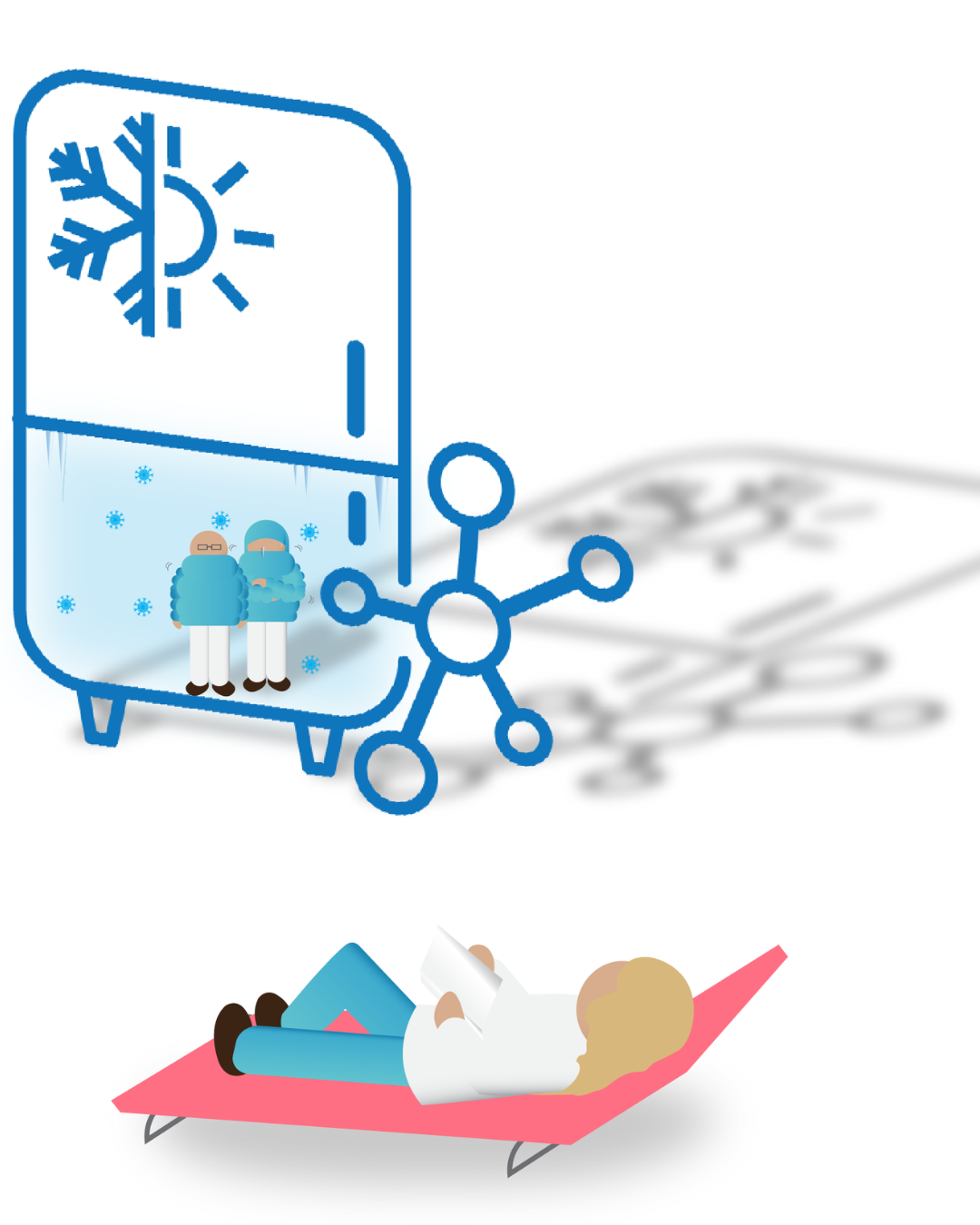
Product Storage Conditions
Storage conditions - temperature, light exposure, humidity - directly affect product quality and safety. Stability studies determine appropriate parameters and packaging requirements. Use of cold chains, such as fridges and freezers help the control of environmental conditions to ensure that the product's integrity is maintained from manufacture through to final use in the patient.
If you need an offline read, take away our guide here.
For more information on how we help, click here.